Understanding and Managing Adult Phimosis
Are you having trouble retracting your foreskin? You might be facing what’s called “Phimosis”
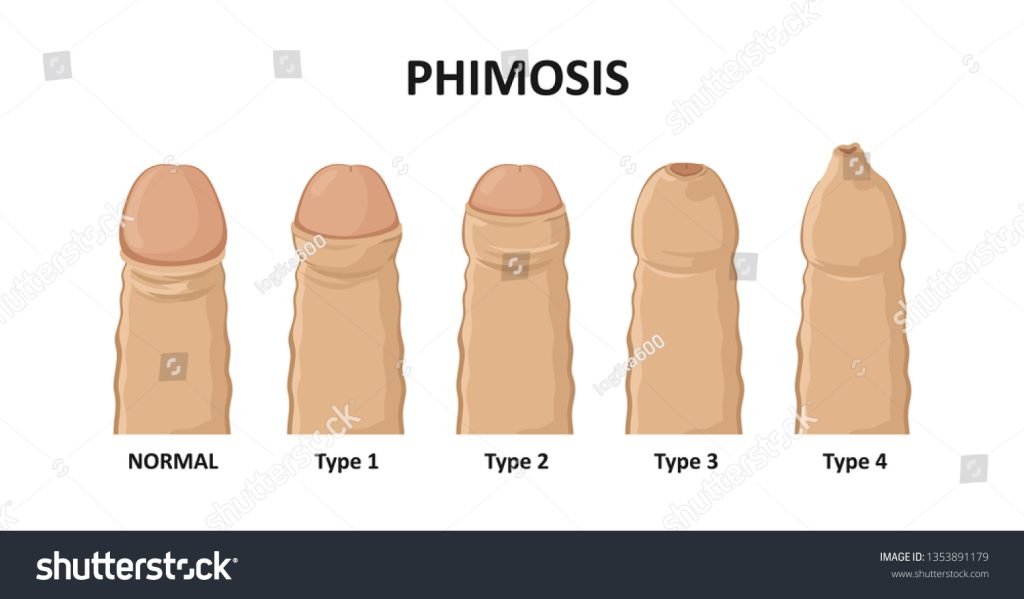
Phimosis refers to the inability to retract the foreskin (prepuce) over the glans penis in uncircumcised males. While physiologic phimosis is common among newborns and typically resolves with age, pathologic phimosis affects individuals beyond childhood and may require treatment.
Pathologic phimosis in adults can manifest as a tight foreskin, causing discomfort, pain, and functional issues such as difficult urination, painful erections, and increased susceptibility to infections. Causes of pathologic phimosis include:
Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans (BXO): Scarring of the foreskin due to inflammation and narrowing of blood vessels.
Poor hygiene: Accumulation of smegma beneath the foreskin, promoting bacterial growth and inflammation.
Diabetes Mellitus: Increased susceptibility to infections due to elevated glucose levels.
Chronic inflammation: Recurrent infections or inflammation of the foreskin and glans.
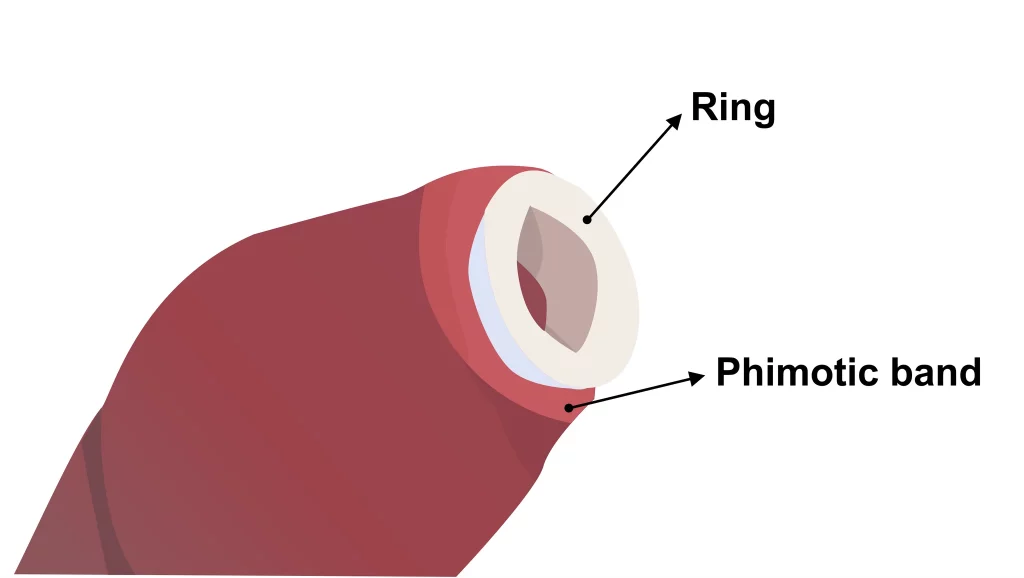
Spotting the Difference: Phimosis vs. Paraphimosis
While we’ve shed light on phimosis, it’s also worth noting another condition: paraphimosis. Unlike phimosis where the foreskin can’t be pulled back, paraphimosis is when the retracted foreskin can’t return to its original position, often causing painful swelling. Always consult a medical professional if you suspect either condition.
What are the treatment options for phimosis in adults?
Phimosis can be managed through various treatment options depending on the severity and underlying causes. Here are some common approaches:
Topical Steroid Creams:
Steroid creams can help soften the foreskin and facilitate retraction. They are applied to the tight ring of the foreskin to reduce inflammation and promote stretching.
Surgery:
Circumcision, which involves the full or partial removal of the foreskin, is a surgical option for severe cases of phimosis that do not respond to conservative treatments. Full circumcision involves removing all of the foreskin, while partial circumcision removes only the tight part.
Preputioplasty:
This is a surgical procedure that preserves the foreskin while addressing phimosis. It involves techniques to widen the tight foreskin opening without removing the entire foreskin.
Dilation and Stretching:
Gentle preputial retractions carried out by a doctor can help stretch the foreskin and promote retraction. This nonsurgical adhesiolysis is found to be effective, safe, and cost-effective for treating phimosis.
Balloon Stretching:
A novel technique involving daily application of balloon stretching can help relax the foreskin over time, making it easier to retract. This method aims to preserve the foreskin while treating phimosis.
Proper Hygiene:
Good hygiene practices, including gentle cleaning of the penis and under the foreskin with warm water, are essential for preventing infections and maintaining skin health.
The Aftermath: Potential Complications
Not treating phimosis can lead to several phimosis complications. For instance:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Difficulty in urination can sometimes lead to UTIs.
Balanitis: This inflammation of the glans can sometimes be a result of untreated phimosis.
Painful Erections: In severe cases, phimosis can make erections painful.
Get timely treatment for optimal penile health–
Individuals with adult phimosis must consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific conditions and needs. Early intervention and appropriate management can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall penile health.
Author

