Gynecomastia- All that you need to know about it!
Trigger warning!: This article contains information related to drug abuse. Having an enlarged breast for a man sometimes may be embarrassing from a societal perspective but hang on! It is common in every age group. Gynecomastia (pronounced: guy-nuh-koh-MAS-tee-uh) is a non-cancerous condition that causes an enlargement of breast tissue in men or boys. There may be an uneven growth in breasts. Breasts lumps are formed which can be seen as a pea-sized growth underneath the nipples. It can affect any man at any age but usually occurs during the newborn period, puberty and older adulthood. |
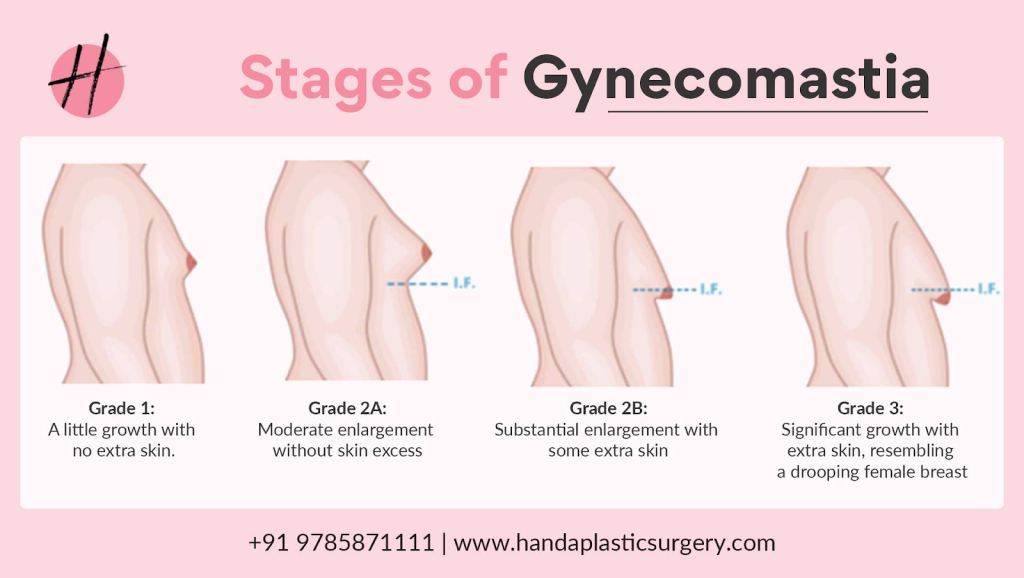
What Causes Gynecomastia?
It is often caused by a hormonal imbalance between the female hormone (oestrogen) and the male hormone (testosterone). A small amount of estrogen, the hormone that regulates breast growth, is produced in men’s bodies. If it is produced in excess amounts or there is low testosterone (male hypogonadism), one or both breasts may witness enlargement.
It can also occur as a side effect of some medicines, such as antidepressants, antibiotics, chemotherapy, prostate cancer medicines, ulcer or cardiovascular medicines. Intake of illegal drugs, such as anabolic steroids, heroin, or marijuana can also lead to gynecomastia.
Signs and Symptoms
Gynecomastia is a condition characterized by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. Symptoms may include:
- Swollen or Enlarged Breasts: The most noticeable symptom is the presence of swollen or larger breast tissue.
- Tenderness or Sensitivity: The breasts may feel tender or sensitive to touch.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some individuals may experience pain or discomfort in the affected breast tissue.
- Uneven Breast Growth: Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, and the growth may be uneven.
- Nipple Changes: The nipples may change such as becoming larger, protruding more, or appearing different than usual.
If you experience these symptoms, consulting with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management is recommended.
Gynecomastia VS Pseudogynecomastia
Don’t mistake pseudo-gynecomastia for gynecomastia!
Pseudogynecomastia is a condition in which men develop fatty tissues around, under or behind nipples. This happens mostly with obese people.
Pseudogynecomastia | Gynecomastia | |
Condition(s) | Fatty breasts. | Enlarged or swollen breasts with lumps. |
Primary cause | Excess fat deposition. | Hormonal imbalance. |
Secondary causes | Obesity, poor eating habits, and/or lack of exercise. | Side effects of some medicines or drug abuse. |
Sensitivity | Breasts are mushy to the touch and without tenderness. | Breasts feel tender to the touch. |
Discomfort | No specific discomfort such as pain and swelling, | Discomfort may be felt. |
Don’t worry! If you have pseudogynecomastia, just maintain a healthy diet and burn that fat!!
Alarming Time! ~ When to Consult a Doctor?
Consider calling a doctor under the following conditions:
Breast lump, breast pain or unusual breast changes.
Itchy breast or underarm area.
Nipple discharge.
How to Get Treated?
- Give Time and Observe: Gynecomastia happens mostly in adolescence. So, it usually goes away without any treatment.
- Stop Medications: If it is caused by a medicine(s), either discontinue its usage or switch to its alternative.
- Treat that Disease: If it is caused by a disease, then treatment is a must.
- Hormone Therapy: If it is caused by hormonal imbalances, hormone therapy may be used to treat gynecomastia. Selective oestrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) such as tamoxifen or raloxifene may be used to help reduce breast tissue growth.
- Change lifestyle: In cases where gynecomastia is associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity or excessive alcohol consumption, making lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise regimen may help reduce breast tissue enlargement.
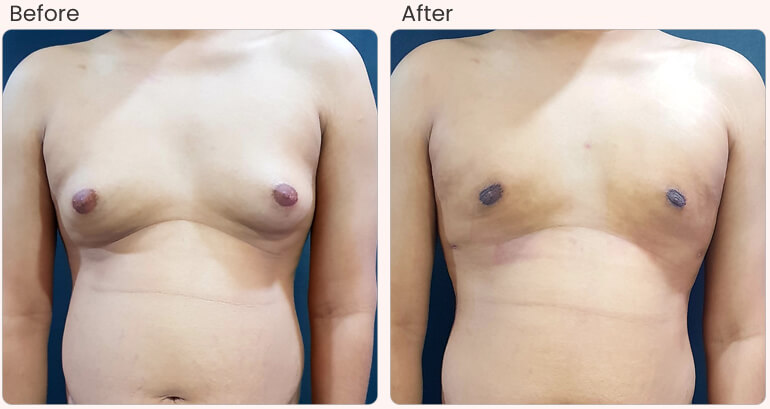
- Surgery: Plastic surgeries may also be referred, such as mastectomy and liposuction.
This article is for informational purposes only. This information does not constitute medical advice or diagnosis. Please consult your doctor for professional guidance.
Author


1 thought on “Gynecomastia – All that you need to know about it!”
Really a good article for creating awareness about this problem among the adolescent age group as this is becoming a measure issue due to social stigma in our society